Resource Library
Informing Reproductive and Child Health Social and Behavior Change Programs: Findings from a household survey in Nepal
In Nepal, SHOPS Plus focuses on building the technical capacity and financial sustainability of the CRS Company, a Nepalese social marketing organization and key USAID partner. CRS leads the Ghar Ghar Maa Swasthya (GGMS), or Healthy Homes project, in 49 urban and rural districts of Nepal (nearly two-thirds of the country) from both hill and mountain regions. The GGMS project aims to increase access to family planning products and improve child health indicators through marketing and distribution of subsidized family planning and child health products. As part of the GGMS project, CRS is implementing community-based social and behavior change activities called the Remote Area Initiative (RAI) in certain parts of four hill districts. The second phase of CRS’ RAI program will focus on social and behavior change activities related to family planning access and choice, diarrhea prevention and treatment, use of antenatal care services and facility delivery, and uterine prolapse prevention and treatment. The RAI program has a variety of social and behavior change components including interpersonal communication and community events. In contrast, the larger GGMS program focuses solely on product marketing and distribution.
SHOPS Plus conducted a knowledge, attitudes, and practices baseline survey in the GGMS and RAI districts.This report presents outcomes from the baseline GGMS and RAI surveys as well as recommendations to inform CRS’ GGMS and RAI programs. Key outcomes included in this report are the modern contraceptive prevalence rate, the percentage of caregivers who used ORS and zinc to treat diarrhea in children under 5, the percentage of pregnant women who attended four or more antenatal care visits, the percentage of women who delivered in health centers, knowledge of hand washing, and the percentage of households that treat their drinking water.
Resource Type : Report
Country : Nepal
Year : 2018-11-28T16:30:00
Language : English
Project : SHOPS Plus

Resource Library
Use of the opportunity, ability, and motivation behavior change framework to generate family planning demand in rural settings: Findings from Nepal
In rural Nepal, the modern contraceptive prevalence rate is 41%, and the unmet need for family planning is 25% (DHS, 2016). SHOPS Plus supports the Nepal CRS Company (CRS), a social marketing organization, to increase modern contraception access and use in rural, underserved communities. To catalyze reductions in unmet need, CRS’s Ghar Ghar Maa Swasthya (GGMS) project in rural Nepal generates family planning demand through behavior change communication and increases contraceptive access through social marketing.
The SHOPS Plus team conducted a knowledge, attitudes, and practices (KAP) survey in the GGMS areas to understand barriers to family planning uptake using the opportunity, ability, and motivation (OAM) behavior change framework (Chapman, 2004). The OAM framework was developed within the context of social marketing and focuses on mutable behavioral determinants that social marketing interventions and behavior change communication can influence. Our findings present key OAM determinants of and impediments to increased contraceptive access and use in extremely remote areas. This study can inform family planning programs throughout rural South Asia and is vitally important and timely given the Commission on the Status of Women’s 2018 priority of achieving gender equality for rural women.
SHOPS Plus research, monitoring, and evaluation director for Nepal Sujan Karki presented the poster at the International Conference on Family Planning on November 14 in Kigali, Rwanda.
Learn more about the research.
Resource Type : Presentation
Country : Nepal
Year :
Language : English
Project : SHOPS Plus

Resource Library
Sources for Sick Child Care in Nepal (Presentation)
The private sector is the primary source of care in Nepal; however, care-seeking patterns vary by socioeconomic status. Understanding if and where sick children are taken for care is critical to improve case management interventions. This slide deck presents secondary analysis of the 2016 Nepal Demographic and Health Survey to examine where treatment or advice is sought for sick children who experience at least one of three treatable illnesses: fever, acute respiratory infection, or diarrhea. These illnesses represent some of the leading causes of death in children under five years old.
Resource Type : Presentation
Country : Nepal
Year : 2018-07-25T12:00:00
Language : English
Project : SHOPS Plus

Resource Library

Care Seeking for Child Illnesses A New Look (Asia Webinar)
On Tuesday, July 31, USAID and its flagship private sector health project, SHOPS Plus, hosted the last of its regional webinars that examined trends in the Asia region and highlighted country examples with local speakers from Nepal, Burma, and India.
Presenters:
- Shilu Adhikari of USAID/Nepal
- Ma Myo Aye of USAID/Burma
- Sachin Gupta of USAID/India
Resource Type : Webinar
Country : India, Nepal
Year : 2018-07-31T07:30:00
Language : English
Project : SHOPS Plus

Resource Library
Sources for Sick Child Care in Nepal
The private sector is the primary source of care in Nepal; however, care-seeking patterns vary by socioeconomic status. Understanding if and where sick children are taken for care is critical to improve case management interventions. This brief presents a secondary analysis of the 2016 Nepal Demographic and Health Survey to examine where treatment or advice is sought for sick children who experience at least one of three treatable illnesses: fever, acute respiratory infection, or diarrhea. These illnesses represent some of the leading causes of death in children under five years old.
Resource Type : Brief
Country : Nepal
Year : 2018-07-31T07:30:00
Language : English
Project :

Resource Library
Global Role of the Private Sector in the Provision of Modern Contraception
This presentation examines the role of the private sector in the provision of modern contraceptives in Asia, Latin America and the Caribbean, and sub-Saharan Africa. It was presented by Jorge I. Ugaz at the SHOPS end-of-project event on June 16, 2015.
Resource Type : Presentation
Country : Nepal, Pakistan
Year : 2015-07-06T00:00:00
Language : English
Project : SHOPS

Resource Library

Advancing Knowledge to Inform Program Design
Minki Chatterji, research director for the SHOPS project, oversees the project’s research portfolio, which includes global research, process and impact evaluations, formative research, provider censuses, and qualitative behavioral research. A demographer by training, she has more than 10 years of experience in global health research, including work on family planning and reproductive health, HIV and AIDS, and maternal and child health. In this video, Chatterji discusses the range of SHOPS research and how the project incorporates its research into its programs.
Resource Type : Video
Country : Bangladesh, Benin, Bolivia, Botswana, Ethiopia, Ghana, Haiti, India, Jamaica, Jordan, Kenya, Madagascar, Malawi, Mali, Namibia, Nepal, Pakistan, Paraguay, Peru, Philippines, Russia, Sénégal, Senegal, South Africa, Tanzania, UAR, Uganda, Zambia, Zimbabwe
Year : 2015-04-15T12:00:00
Language : English
Project : SHOPS

Resource Library
National Scale-up of Zinc Promotion in Nepal: Results from a Post-project Population-based Survey
The World Health Organization and the United Nations Children’s Fund recommend using a new oral rehydration solution (ORS) plus zinc supplementation for 10-14 days for the treatment of diarrhoea in children aged less than five years. The Social Marketing Plus for Diarrhoeal Disease Control: Point of Use Water Disinfection and Zinc Treatment (POUZN) project in Nepal was one of the first zinc-promotion projects to move beyond pilot efforts into a scaled-up programme with national-level reach. This study used data from a survey conducted in 26 districts in Nepal in 2008 to examine zinc-use behaviour, knowledge, and beliefs of caregivers of children aged less than six years, other diarrhoea-treatment practices, and recollection of project communication messages. The results of the survey indicated that, by six months following the onset of a zinc-promotion campaign, the majority (67.5%) of children (n=289), aged less than six years, with diarrhoea were treated with ORS, and 15.4% were treated with zinc. Over half (53.1%) of all caregivers (n=3,550) interviewed had heard about zinc products; most (97.1%) of those who had heard of zinc knew that zinc should be used for the treatment of diarrhoea. Zinc-related knowledge and behaviours were positively associated with recall of communication messages. Children whose caregivers recalled the mass-media message that zinc should be used for 10 days [odds ratio (OR)=2.02, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.85-2.19] and whose caregivers perceived that zinc is easy to obtain (OR=1.76, 95% CI 1.49-2.09) were more likely to be treated with zinc for 10 days, along with ORS. The findings demonstrated that mass media play an important role in increasing caregivers’ knowledge about zinc and encouraging trial and correct use. Future efforts should also focus on understanding the factors that motivate providers to continue recommending antibiotics and antidiarrhoeals instead of zinc. These findings are being used for informing the design and implementation of zinc programmes in other developing countries with a high prevalence of diarrhoea.
Resource Type :
Country : Nepal
Year : 2011-06-29T00:00:00
Language : English
Project : SHOPS

Resource Library
Nepal (2008): Zinc TRaC Survey
This zinc-used focused household survey was conducted in July-October 2008 with a total of 3550 respondents in POUZN program districts in order to provide quantifiable data to assist program managers to monitor and evaluate the POUZN program in Nepal. The study provided guidance for the development of an evidence-based, strategic, cost-effective behavior change intervention focused on increasing the use of zinc along with ORS (oral rehydration salts) for the treatment of diarrhea in children five years of age and under.
The survey found the 6.9% of the children in the sampled households had diarrhea in last two weeks, 9.7% children had diarrhea in last one month and 1.1% had diarrhea with blood. About half of the respondents had heard about zinc for the treatment of diarrhea. Seventy-two percent of the children who had diarrhea were given ORS, 16.6% of the children received zinc and 14.6% received zinc along with ORS. The most reliable and valid behavioral determinants for use of zinc for the treatment of diarrhea were found to be: availability and outcome expectations.
The following key program recommendations are provided:
- Interventions should attempt to improve the opportunity to use zinc by increasing the availability of the product. Results show that mothers/ care-givers with a better perception of availability are more likely to use zinc for the treatment of diarrhea as compared to their counterparts.
- Interventions should attempt to increase the motivation to use zinc by addressing outcome expectations. Programmers should attempt to improve the belief that zinc is effective in the treatment of diarrhea in children.
Resource Type : Brief
Country : Nepal
Year : 2008-11-01T00:00:00
Language : English
Project : SHOPS

Resource Library
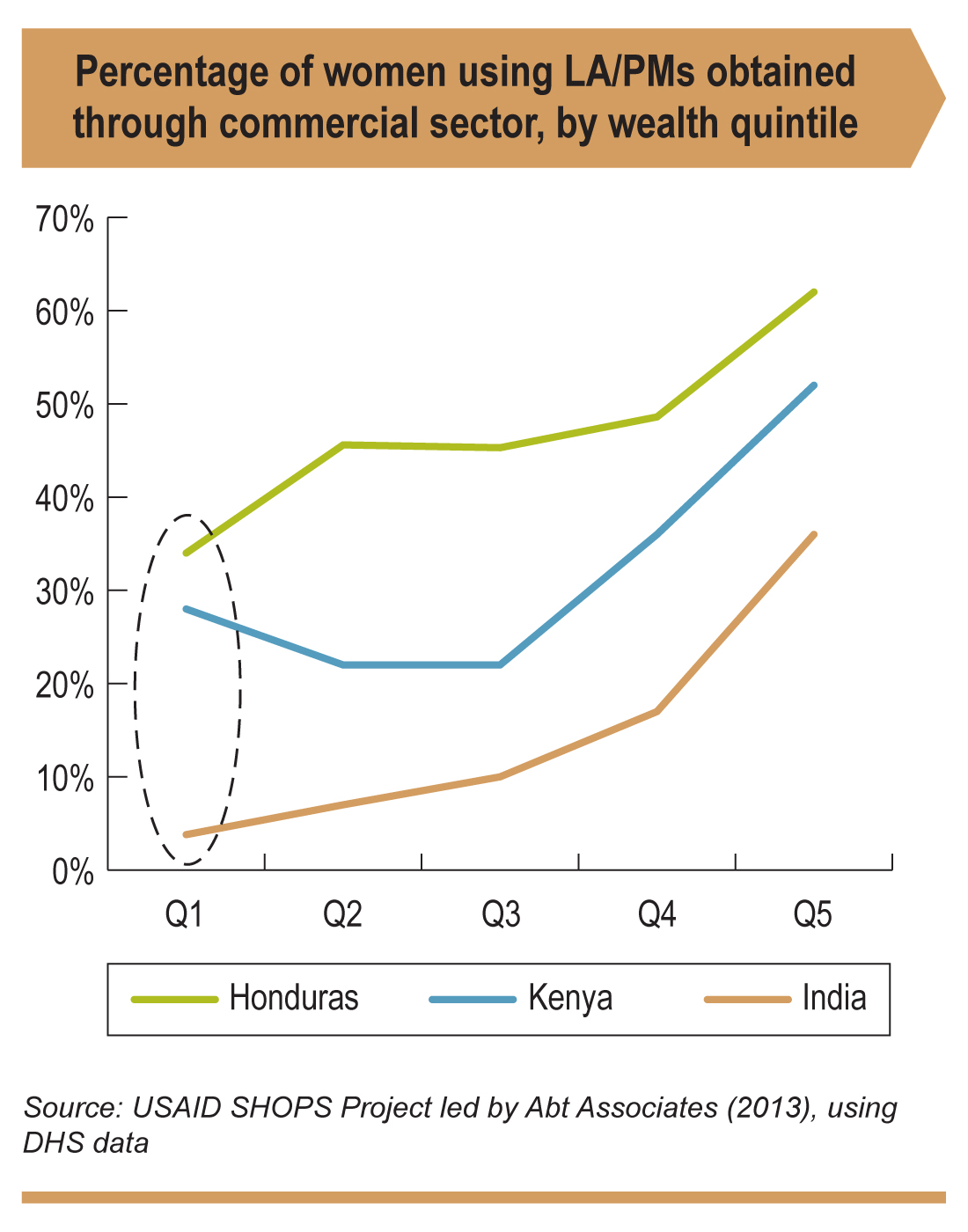
Understanding the Association between Wealth, Long-Acting Contraception, and the Private Sector
An analysis of 14 Demographic and Health Surveys revealed that wealthier women are more likely than poorer women to use long-acting or permanent contraceptive methods instead of short-acting methods. They are also more likely to obtain these methods from the commercial sector. However, in some countries, a substantial minority of women from low and middle wealth quintiles uses the commercial sector for long-acting or permanent contraceptive methods.
Resource Type : Brief
Country : Bangladesh
Year : 2013-11-13T14:52:00
Language : English
Project : SHOPS
Pagination
- Previous page
- Page 3
- Next page