Resource Library
Results and Lessons Learned from Household Surveys in Nepal, Benin, Madagascar, and Pakistan
Integrating Zinc into Diarrhea Management e-Conference Panel 2 presentation by Kathryn Kohler Banke, Abt Associates.
Resource Type : Presentation
Country : Benin, Madagascar, Nepal, Pakistan
Year : 2011-06-01T00:00:00
Language : English
Project : SHOPS

Resource Library
Social Marketing Plus for Diarrheal Disease Control: Point-of-Use Water Disinfection and Zinc Treatment (POUZN) Project
The Social Marketing Plus for Diarrheal Disease Control: Point-of-Use Water Disinfection and Zinc Treatment (POUZN) Project is a $12 million project funded by USAID that was designed to expand access to and use of point-of-use (POU) water disinfection and zinc products for the prevention and treatment of diarrhea through private sector channels. The POUZN project was implemented from October 2005 through November 2010 by Abt Associates Inc. in collaboration with Population Services International (PSI). Over the life of the project, it worked in 13 countries. A full POU program was carried out in six countries (Benin, Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), Haiti, Kenya, Malawi, and Rwanda), full zinc promotion programs were carried out in four countries (Benin, Madagascar, Nepal, and Pakistan), and technical assistance was provided in four additional countries (Angola, Bangladesh, Cambodia, and Senegal).
Resource Type : Report
Country : Bangladesh, Benin, Cambodia, Democratic Republic of Congo, Haiti, Kenya, Madagascar, Malawi, Nepal, Pakistan, Rwanda, Senegal
Year : 2011-06-10T00:00:00
Language : English
Project : SHOPS

Resource Library

Pakistan television TV zinc promotion
A video contributed as a resource for the SHOPS Zinc e-Conference held on June 1-2, 2011.
Resource Type : Video
Country : Pakistan
Year : 2011-06-01T00:00:00
Language : English
Project : SHOPS

Resource Library
Zinc Supplementation for the Treatment of Diarrhea in Infants in Pakistan, India and Ethiopia
OBJECTIVE: This randomized, placebo controlled trial was designed to assess the safety and efficacy of 10-mg zinc supplementation for the treatment of acute diarrhea in infants. METHODS: A total of 1110 infants aged 28 days to 5 months with acute diarrhea were enrolled and randomized to receive eit her zinc (n = 554) or placebo (n = 556) for 14 days. Diarrhea history, anthropometric status, breast-feeding status and socioeconomic indicators were assessed at baseline. The homes of all infants were visited every 3 days until the diarrhea episode was over. The number of stools, presence of blood and additional illnesses were recorded daily. RESULTS: The geometric mean duration of the diarrhea episode was 0.21 days longer among infants receiving zinc versus those receiving placebo, but this was not statistically significant and no difference was observed after controlling for sex, exclusive breast-feeding and length for age Z score. There were no differences in any subgroup (ie, sex, baseline length for age Z score, exclusive breast-feeding or site after controlling for the remaining subgroup variables). There were no differences in reported stool frequency or among the proportion of episodes lasting longer than 7 days. Rates of vomiting were similar in the zinc and placebo groups. CONCLUSIONS: Young infants do not appear to benefit from zinc supplementation for the treatment of diarrhea.
Resource Type : Other
Country : Ethiopia, India, Pakistan
Year : 2006-09-29T12:15:00
Language : English
Project : SHOPS

Resource Library
3rd International Zinc Conference (24-25 April 2006): Recent Advances in Scaling up Zinc
This web link will take the reader to the ICDDRB website and access to all presentations from the meeting where lessons learned were shared from India, Nepal, Cambodia, Indonesia, East Timor, Pakistan and Uganda. Important recent research findings that have emerged over the past year and usage and effectiveness of zinc treatment in emergency settings were also highlighted.
Resource Type : Other
Country :
Year : 2006-04-24T10:00:00
Language :
Project : SHOPS

Resource Library
DFID Private Sector Report
DFID Private Sector Report
Resource Type : Report
Country : Bangladesh, India, Kenya, Pakistan, Tanzania, Uganda, Vietnam
Year : 2006-06-12T14:30:00
Language : English
Project : SHOPS

Resource Library
The Impact of Private Clinic Networks on Client Service Access and Quality: Evidence from Ethiopia, India and Pakistan
PowerPoint presentation from PSP-One's GHC Expert Panel: Expanding Health Service Access, Quality, and Equity in Developing Countries: The Role of the Private Sector.
Resource Type : Presentation
Country : Ethiopia, India, Pakistan
Year : 2006-06-09T14:30:00
Language : English
Project : SHOPS

Resource Library
Safe Drinking Water Alliance Fact Sheet
These links takes the reader to the Johns Hopkins University Center for Communication Programs website on safe water and to the JHU CCP website for the Safe Drinking Water Alliance and its fact sheet.
Resource Type : Brochure/Postcard
Country :
Year : 2004-03-01T12:15:00
Language :
Project : SHOPS

Resource Library
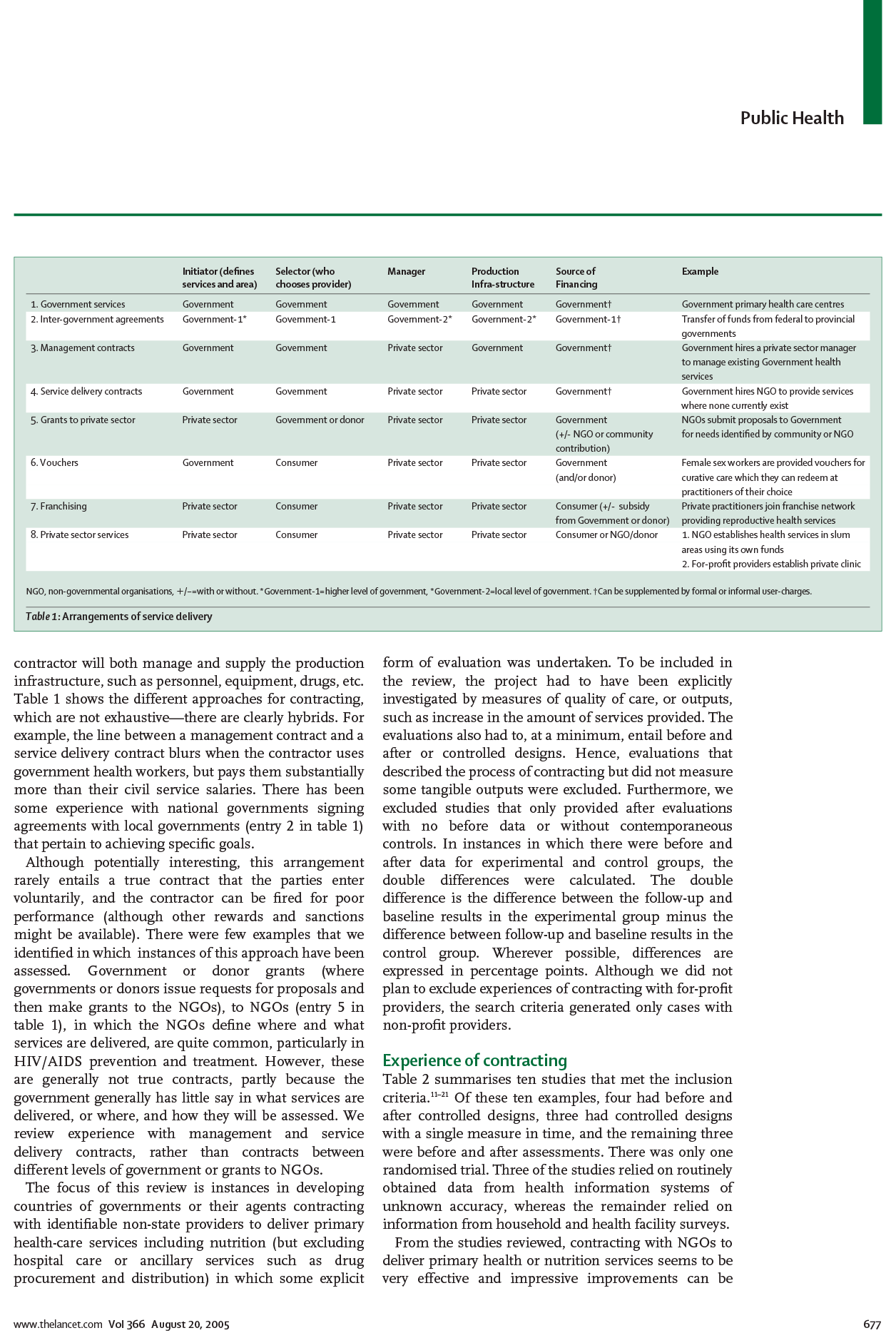
Buying Results? Contracting for Health Service Delivery in Developing Countries
To achieve the health-related Millennium Development Goals, the delivery of health services will need to improve. Contracting with non-state entities, including non-governmental organizations (NGOs), has been proposed as a means for improving health care delivery, and the global experience with such contracts is reviewed here. The ten investigated examples indicate that contracting for the delivery of primary care can be very effective and that improvements can be rapid. These results were achieved in various settings and services. Many of the anticipated difficulties with contracting were either not observed in practice or did not compromise contracting effectiveness. Seven of the nine cases with sufficient experience (greater than 3 years' elapsed experience) have been sustained and expanded. Provision of a package of basic services by contractors costs between roughly US$3 and US$6 per head per year in low-income countries. Contracting for health service delivery should be expanded and future efforts must include rigorous evaluations.
Resource Type : Report
Country : Bangladesh, Bolivia, Cambodia, Guatemala, Haiti, India, Madagascar, Pakistan
Year : 2005-08-20T14:15:00
Language : English
Project : SHOPS

Resource Library
Prevention of diarrhea and pneumonia by zinc supplementation in children in developing countries: pooled analysis of randomized controlled trials
Study assessed the effects of zinc supplementation in the prevention of diarrhea and pneumonia with the use of a pooled analysis. Study concluded that zinc supplementation in children in developing countries is associated with substantial reduction in the rates of diarrhea and pneumonia, the two leading causes of death in these settings.
Resource Type : Other
Country : Bangladesh, Guatemala, India, Jamaica, Pakistan, Peru, Vietnam
Year : 1999-01-01T15:15:00
Language : English
Project : SHOPS
Pagination
- Previous page
- Page 4
- Next page